Description
Java is a high-level, object-oriented, general-purpose programming language designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. Created by James Gosling and released by Sun Microsystems in 1995 (now owned by Oracle), Java allows developers to write code once and run it anywhere (WORA) due to its platform-independent nature enabled by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Java is widely used in enterprise applications, Android development, web services, financial systems, and large-scale distributed environments. Its syntax is heavily influenced by C/C++ but offers automatic memory management, exception handling, and strong type checking, making it a safer alternative.
Core Concepts
- Platform Independence: Java code is compiled into bytecode, which runs on any device with a compatible JVM.
- Object-Oriented: Supports encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Robust and Secure: Features like garbage collection, runtime checking, and security APIs.
- Multi-threaded: Built-in support for concurrent execution.
- Architecture Neutral: Bytecode can be executed on any processor architecture.
Java Architecture
- Source Code (
.java): Written by the developer. - Compiler (
javac): Converts.javafiles into bytecode.classfiles. - Bytecode: Platform-independent intermediate code.
- JVM: Executes bytecode on the host machine.
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment): Includes JVM and standard libraries.
- JDK (Java Development Kit): Includes JRE plus development tools.
Hello World Example
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}Java Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Simple | Easy to learn, clean syntax |
| Secure | No pointers, has bytecode verifier and security APIs |
| Portable | Platform-independent bytecode |
| High Performance | JIT compiler improves execution speed |
| Distributed | Supports RMI, CORBA, web services |
| Dynamic | Loads classes at runtime |
Java Editions
- Java SE (Standard Edition): Core functionalities for desktop and server apps.
- Java EE (Enterprise Edition): APIs for distributed and enterprise applications.
- Java ME (Micro Edition): For embedded and mobile devices.
- JavaFX: For building rich desktop applications with GUIs.
Common Java APIs
java.lang: Core classes likeString,Math,Objectjava.util: Data structures (ArrayList, HashMap), Collections frameworkjava.io/java.nio: File and input/output operationsjava.net: Networking capabilitiesjava.sql: Database connectivity using JDBCjava.time: Date and time API
Object-Oriented Principles
Java is built around the four main OOP principles:
- Encapsulation: Grouping data and behavior
- Inheritance: Creating new classes from existing ones
- Polymorphism: Dynamic method dispatch
- Abstraction: Hiding internal implementation details
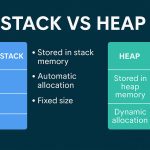
Memory Management
Java uses an automatic garbage collection mechanism:
- Heap Memory: For object storage
- Stack Memory: For method calls and local variables
- Garbage Collector: Frees memory used by unreachable objects
Exception Handling
Java provides robust error handling via try-catch-finally blocks:
try {
int result = 10 / 0;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("Cannot divide by zero!");
} finally {
System.out.println("Cleanup code");
}Multithreading
Java’s built-in threading model allows concurrent execution:
Threadclass andRunnableinterface- Synchronization blocks (
synchronizedkeyword) ExecutorServicefor thread pools
Popular Java Frameworks
- Spring: Enterprise application framework
- Hibernate: ORM for database interactions
- Apache Struts: MVC-based web app framework
- Maven/Gradle: Build automation tools
Java in Industry
Java powers large-scale applications:
- Banking and Finance: Backend systems, transaction management
- Android Apps: Core language for app development (alongside Kotlin)
- Enterprise Web Services: RESTful/SOAP APIs
- Big Data and Cloud: Hadoop, Spark, Kafka integrations
Tools and IDEs
- IDEs: IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, NetBeans
- Build Tools: Maven, Gradle, Ant
- Testing Tools: JUnit, TestNG
- Profiling Tools: VisualVM, JConsole
Summary
Java is a powerful, versatile, and enduring language used across industries for building scalable, secure, and robust applications. Its combination of simplicity, object-orientation, and cross-platform support has made it one of the most influential programming languages in history. Mastering Java opens the door to enterprise development, Android apps, cloud computing, and beyond.